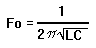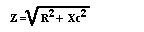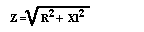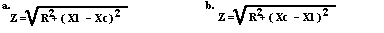Basic Electronic Formulas and Facts
Ohm's Law
- E = Voltage - measured in Volts
- I = Current - measured in Amperes
- R = Resistance - measured in Ohms
- E = I * R , answer in Volts
- I = E/R, answer in Amperes
- R = E/I, answer in Ohms
back to top of page
Resistor Networks
- Resistors are labeled by a # following the R : R1...R2...Rn
- Rn = Continues for all the resistors you have.
- Rt = Resistance total
- Resistors in SERIES add : Rt = R1 + R2 +R3....+ Rn
- Two (2) Resistors in PARALLEL : Rt = ( R1 * R2)/(R1 + R2) This the Product divided by the Sum
- More than Two Resistors in PARALLEL: Rt = 1/ (1/R1 + 1/R2...+1/Rn) This is called the reciprocal formula
- Another form of this formula is : 1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2.....+1/Rn
back to top of page
Inductor Networks
- The rules for Inductors are exactly like those for Resistors
- Inductors are labeled by a # following the L : L1...L2...Ln
- Ln = Continues for all the Inductors you have.
- Lt = Inductance total
- Inductors in SERIES add : Lt = L1 + L2 +L3....+ Ln
- Two (2) Inductors in PARALLEL : Lt = ( L1 * L2)/(L1 + L2) This the Product divided by the Sum
- More than Two Inductors in PARALLEL: Lt = 1/ (1/L1 + 1/L2...+1/Ln) This is called the reciprocal formula
- Another form of this formula is : 1/Lt = 1/L1 + 1/L2.....+1/Ln
back to top of page
Capacitor Networks
- The rules for Capacitor Networks are exactly opposite for those
of Resistors and Inductors.
- Capacitors are labeled by a # following the C : C1...C2...Cn
- Cn = Continues for all the Capacitors you have.
- Ct = Capacitance total
- Capacitors in PARALLEL add : Ct = C1 + C2 +C3....+ Cn
- Two (2) Capacitors in SERIES : Ct = ( C1 * C2)/(C1 + C2) This is the Product divided by the Sum
- More than Two Capacitors in SERIES: Ct = 1/ (1/C1 + 1/C2...+1/Cn) This is called the reciprocal formula
- Another form of this formula is : 1/Ct = 1/C1 + 1/C2.....+1/Cn
back to top of page
Watt's Law
- P = Power - measured in Watts
- I = Current - measured in Amperes
- E = Voltage - measured in Volts
- R = Resistance - measured in Ohms
- P = I * E, answer in Watts - (easy as "pie")
- P = I*I*R, answer in Watts -( read as I squared R)
- P = E*E/R, answer in Watts -( read as E squared, divided by R)
- Note: Use Ohm's Law to derive other formulas for I , R, and E, using the formulas above.
back to top of page
Calculating Reactance
- Inductive Reactance
- Pi =
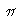 = 3.14
= 3.14
- f = Frequency, in Hertz
- L = Inductance of coil, in Henries
- Xl = Inductive Reactance, in Ohms
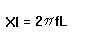 , answer in Ohms
, answer in Ohms
- Note: Xl is a linear function, it increases as frequency or inductor value increases.
back to top of page
- Capacitive Reactance
- Pi =
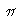 = 3.14
= 3.14
- f = Frequency, in Hertz
- C = Capacitance in Farads
- Xc = Capacitive Reactance, in Ohms
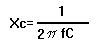 , answer in Ohms
, answer in Ohms
- Note: Xc is inversely proportional to frequency and capacitance. If either frequency or
capacitance increase, Xc decreases.
back to top of page
Resonance in RLC Series Circuit
back to top of page
Wavelength
back to top of page
Frequency and Time
- f is the Frequency in Hertz/Second or Cycles/Second
- t is time in Seconds
- f = 1/t , answer in Hertz/Second or Cycles/Second.
- t = 1/f , answer in Seconds
back to top of page
Impedance of a Circuit
- Xc = Capacitive Reactance, in Ohms
- Xl = Inductive Reactance, in Ohms
- R = Resistance, in Ohms
- Z = Impedance, in Ohms
- For a Capacitive circuit
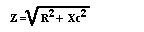
- For an Inductive Circuit
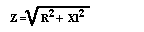
- Rules for when you have a circuit with both Capacitive and Inductive Reactances
- When Xl is larger than Xc use the formula in figure (a)
, If Xc is Larger than Xl use the formula in Figure (b).
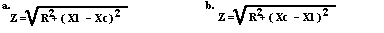
back to top of page


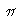 = 3.14
= 3.14
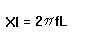 , answer in Ohms
, answer in Ohms
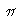 = 3.14
= 3.14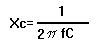 , answer in Ohms
, answer in Ohms
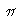 = 3.14
= 3.14