duty cycle:
- In an ideal pulse train, i.e., one having rectangular pulses, the ratio of the pulse duration to the pulse period.
Note: For example, the duty cycle is 0.25 for a pulse train in which the pulse duration is 1 s and the pulse period is 4 s.
- The ratio of (a) the sum of all pulse durations during a specified period of continuous operation to (b) the total specified period
of operation.
- In a continuously variable slope delta (CVSD) modulation converter, the mean proportion of binary "1" digits at
the converter output in which each "1" indicates a run of a specified number of consecutive bits of the same polarity in the digital
output signal.
- In a periodic phenomenon, the ratio of the duration of the phenomenon in a given period to the period. Note:
In a piece of electrical equipment, e.g., an electric motor, the period for which it may be operated without deleterious effects,
e.g., from overheating.
pulse train: A series of pulses having similar characteristics. Synonym pulse string.
pulse period: The reciprocal of the pulse repetition rate.
pulse duration:
- In a pulse waveform, the interval between (a) the time, during the first transition, that the pulse amplitude
reaches a specified fraction (level) of its final amplitude, and (b) the time the pulse amplitude drops, on the last transition, to the
same level. Note: The interval between the 50% points of the final amplitude is usually used to determine or define pulse
duration, and this is understood to be the case unless otherwise specified. Other fractions of the final amplitude, e.g., 90% or
1/e (where e = 2.71828. . .), may also be used, as may the root-mean-square (rms) value of the pulse amplitude. Deprecated
synonyms pulse length, pulse width.
- In radar, measurement of pulse transmission time in microseconds, that is, the time
the radar's transmitter is energized during each cycle.
duty cycle
continuous operation:
- Operation in which certain components, such as nodes, facilities, circuits, or equipment, are in an
operational state at all times. Note: Continuous operation usually requires that there be fully redundant configuration, or at least
a sufficient X out of Y degree of redundancy for compatible equipment, where X is the number of spare components and Y is
the number of operational components.
- In data transmission, operation in which the master station need not stop for a reply
from a slave station after transmitting each message or transmission block.
continuously variable slope delta (CVSD) modulation: A type of delta modulation in which the size of the steps of the
approximated signal is progressively increased or decreased as required to make the approximated signal closely match the
input analog wave.
binary:
- Pertaining to a selection, choice, or condition that has two possible different values or states. Typically zero (0 - 0 Volts - low) and one (1 - 1 Volt - high)
- Pertaining to a fixed
radix numeration system that has a radix of 2.
output:
- Information retrieved from a functional unit or from a network, usually after some processing.
- An output state, or
sequence of states.
- Pertaining to a device, process, or channel involved in the production of data by a computer or by any of
its components.
run: The execution of one or more computer jobs or programs.
digital: Characterized by discrete states.
signal:
- Detectable transmitted energy that can be used to carry information.
- A time-dependent variation of a
characteristic of a physical phenomenon, used to convey information.
- As applied to electronics, any transmitted electrical
impulse.
- Operationally, a type of message, the text of which consists of one or more letters, words, characters, signal
flags, visual displays, or special sounds, with prearranged meaning and which is conveyed or transmitted by visual, acoustical,
or electrical means.
waveform: The representation of a signal as a plot of amplitude versus time.
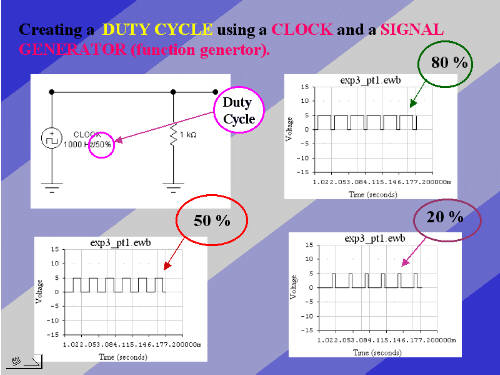
Duty cycle is the proportion of time during which a component, device,
or system is operated. The duty cycle can be expressed as a ratio or as
a percentage. Suppose a disk drive operates for 1 second, then is shut
off for 99 seconds, then is run for 1 second again, and so on. The drive
runs for one out of 100 seconds, or 1/100 of the time, and its duty
cycle is therefore 1/100, or 1 percent.
The more a circuit, machine or component is used, the sooner it will
wear out. Therefore, the higher the duty cycle, the shorter the useful
life, all other things being equal. If the above-mentioned disk drive has
a life expectancy of 1,000,000 hours based on a 1 percent duty cycle,
that same device's expectancy would probably be about 500,000 hours
based on a duty cycle of 2 percent, and 2,000,000 hours based on a
duty cycle of 0.5 percent.
|
